A Comprehensive Guide

Moving to Canada from Pakistan offers numerous opportunities for a better life, including economic prospects, quality education, healthcare, and a multicultural society. This article will explore the best ways to immigrate to Canada from Pakistan, highlighting the most popular immigration pathways and providing essential information for a successful transition.
1. Express Entry System:

The Express Entry system is a popular and efficient way to immigrate to Canada. It includes three main programs: the Federal Skilled Worker Program (FSWP), the Federal Skilled Trades Program (FSTP), and the Canadian Experience Class (CEC). Key points to consider:
The Express Entry System: A Pathway to Canadian Immigration
The Express Entry system has revolutionized the way individuals immigrate to Canada. Introduced in 2015, it has become the primary pathway for skilled workers to obtain permanent residency. This article provides a brief overview of the Express Entry system, its key components, and how it has streamlined the immigration process.
i. Purpose and Benefits:
The Express Entry system was designed to attract skilled workers who can contribute to Canada’s economy. Its key benefits include:
– Efficiency: The system processes applications quickly, with most candidates receiving a decision within six months.
– Flexibility: Express Entry covers three main programs – the Federal Skilled Worker Program (FSWP), the Federal Skilled Trades Program (FSTP), and the Canadian Experience Class (CEC) – allowing individuals with diverse backgrounds to apply.
– Comprehensive Ranking System (CRS): The CRS ranks candidates based on factors such as age, education, work experience, language proficiency, and adaptability. Higher-ranking candidates receive Invitations to Apply (ITAs) for permanent residency.
ii. Eligibility and Requirements:
To be eligible for Express Entry, candidates must meet the following requirements:
– Skilled Work Experience: Candidates must have at least one year of full-time work experience (or equivalent part-time) in a skilled occupation.
– Language Proficiency: Proficiency in English or French is essential. Candidates must take a language test (such as IELTS or CELPIP) and achieve the minimum required scores.
– Educational Credential Assessment (ECA): Candidates must obtain an ECA to verify the equivalency of their foreign educational credentials to Canadian standards.
– Proof of Funds: Candidates must demonstrate sufficient funds to support themselves and their family members upon arrival in Canada.
iii. Express Entry Process:
The Express Entry process involves the following steps:
– Creating an Online Profile: Candidates create an Express Entry profile, providing information about their skills, work experience, education, language proficiency, and other relevant details.
– Comprehensive Ranking System (CRS) Score: Candidates are assigned a CRS score based on their profile information. The CRS score determines their ranking in the Express Entry pool.
– Regular Draws: The Canadian government conducts regular draws from the pool, issuing ITAs to candidates with the highest CRS scores. Candidates who receive an ITA can then apply for permanent residency.
– Application for Permanent Residency: Candidates have 60 days to submit a complete application for permanent residency, including supporting documents and fees.
iv. Provincial Nominee Programs (PNPs):
Provincial Nominee Programs are an integral part of the Express Entry system. Provinces and territories can nominate candidates from the Express Entry pool based on their specific labor market needs. A provincial nomination provides additional CRS points, significantly increasing the chances of receiving an ITA.
2: Federal Skilled Worker Program (FSWP): A Pathway to Canadian Permanent Residency
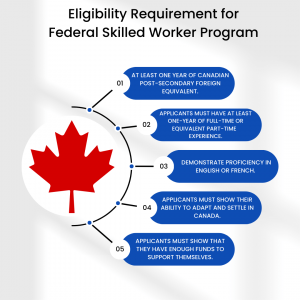
The Federal Skilled Worker Program (FSWP) is a key component of Canada’s Express Entry system, offering skilled workers from around the world an opportunity to obtain permanent residency. This article provides an overview of the FSWP, including its purpose, eligibility criteria, application process, and benefits.
i. Purpose and Benefits:
The FSWP aims to attract skilled workers who can contribute to Canada’s economy. Its key benefits include:
– Permanent Residency: Successful applicants receive Canadian permanent residency, granting them the right to live, work, and study anywhere in Canada.
– Job Market Flexibility: Unlike other immigration programs, the FSWP does not require a job offer from a Canadian employer, providing flexibility in finding employment.
– Access to Social Benefits: Permanent residents have access to Canada’s social benefits, including healthcare, education, and social assistance programs.
ii. Eligibility Criteria:
To be eligible for the FSWP, candidates must meet the following criteria:
– Skilled Work Experience: Candidates must have at least one year of full-time (or equivalent part-time) work experience in a skilled occupation listed under the National Occupational Classification (NOC) system.
– Language Proficiency: Proficiency in English or French is essential. Candidates must take a language test (such as IELTS or CELPIP) and achieve the minimum required scores.
– Educational Qualifications: Candidates must have completed a minimum of a high school diploma or an equivalent foreign credential. Educational credentials are assessed through an Educational Credential Assessment (ECA).
– Proof of Funds: Candidates must demonstrate sufficient funds to support themselves and their family members upon arrival in Canada.
iii. Application Process:
The application process for the FSWP involves the following steps:
– Create an Express Entry Profile: Candidates create an Express Entry profile and indicate their interest in the FSWP. The profile includes information about their skills, work experience, education, language proficiency, and other relevant details.
– Comprehensive Ranking System (CRS) Score: Candidates are assigned a CRS score based on their profile information. The CRS score determines their ranking in the Express Entry pool.
– Invitation to Apply (ITA): Candidates with high CRS scores are invited to apply for permanent residency through regular draws conducted by the Canadian government.
– Submitting the Application: Candidates who receive an ITA have 60 days to submit a complete application for permanent residency, including supporting documents and fees.
iv. Selection Factors:
The FSWP uses a points-based system to assess candidates based on various selection factors, including:
– Age: Younger candidates receive more points.
– Language Proficiency: Higher language test scores result in more points.
– Education: Higher levels of education lead to more points.
– Work Experience: More years of work experience in a skilled occupation result in more points.
– Adaptability: Factors such as previous work or study experience in Canada, a job offer, or family connections in Canada can contribute to additional points.
3:Federal Skilled Trades Program (FSTP): A Pathway to Canadian Permanent Residency
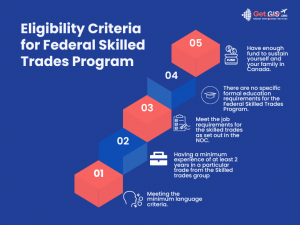
The Federal Skilled Trades Program (FSTP) is an integral part of Canada’s Express Entry system, offering skilled tradespersons from around the world an opportunity to obtain permanent residency. This article provides an overview of the FSTP, including its purpose, eligibility criteria, application process, and benefits.
i. Purpose and Benefits:
The FSTP aims to attract skilled tradespersons who can contribute to Canada’s labor market. Its key benefits include:
– Permanent Residency: Successful applicants receive Canadian permanent residency, granting them the right to live, work, and study anywhere in Canada.
– Job Market Flexibility: Unlike other immigration programs, the FSTP does not require a job offer from a Canadian employer, providing flexibility in finding employment.
– Access to Social Benefits: Permanent residents have access to Canada’s social benefits, including healthcare, education, and social assistance programs.
ii. Eligibility Criteria:
To be eligible for the FSTP, candidates must meet the following criteria:
– Skilled Trade Experience: Candidates must have at least two years of full-time (or equivalent part-time) work experience in a skilled trade listed under the National Occupational Classification (NOC) system.
– Language Proficiency: Proficiency in English or French is essential. Candidates must take a language test (such as IELTS or CELPIP) and achieve the minimum required scores.
– Job Offer or Certificate of Qualification: Candidates must either have a valid job offer of at least one year from a Canadian employer or a certificate of qualification issued by a Canadian provincial or territorial authority.
– Proof of Funds: Candidates must demonstrate sufficient funds to support themselves and their family members upon arrival in Canada.
iii. Application Process:
The application process for the FSTP involves the following steps:
– Create an Express Entry Profile: Candidates create an Express Entry profile and indicate their interest in the FSTP. The profile includes information about their skills, work experience, education, language proficiency, and other relevant details.
– Comprehensive Ranking System (CRS) Score: Candidates are assigned a CRS score based on their profile information. The CRS score determines their ranking in the Express Entry pool.
– Invitation to Apply (ITA): Candidates with high CRS scores are invited to apply for permanent residency through regular draws conducted by the Canadian government.
– Submitting the Application: Candidates who receive an ITA have 60 days to submit a complete application for permanent residency, including supporting documents and fees.
iv. Selection Factors:
The FSTP uses a points-based system to assess candidates based on various selection factors, including:
– Age: Younger candidates receive more points.
– Language Proficiency: Higher language test scores result in more points.
– Work Experience: More years of work experience in a skilled trade result in more points.
– Job Offer or Certificate of Qualification: Having a valid job offer or a certificate of qualification contributes to additional points.
– Adaptability: Factors such as previous work or study experience in Canada, a job offer, or family connections in Canada can contribute to additional points.
– CEC: Aimed at individuals with Canadian work experience, this program allows temporary foreign workers and international graduates to transition to permanent residency. Candidates must meet specific criteria related to work experience, language proficiency, and education.
4:Canadian Experience Class (CEC): A Pathway to Canadian Permanent Residency

The Canadian Experience Class (CEC) is an integral component of Canada’s Express Entry system, offering international graduates and skilled workers with Canadian work experience an opportunity to obtain permanent residency. This article provides an overview of the CEC, including its purpose, eligibility criteria, application process, and benefits.
i. Purpose and Benefits:
The CEC aims to attract individuals who have gained valuable work experience in Canada and have integrated into Canadian society. Its key benefits include:
– Permanent Residency: Successful applicants receive Canadian permanent residency, granting them the right to live, work, and study anywhere in Canada.
– Canadian Work Experience: The CEC recognizes the value of Canadian work experience, making it easier for individuals to transition from temporary to permanent residency.
– Language Proficiency: Candidates with Canadian work experience have already demonstrated language proficiency, which can contribute to a higher Comprehensive Ranking System (CRS) score.
ii. Eligibility Criteria:
To be eligible for the CEC, candidates must meet the following criteria:
– Canadian Work Experience: Candidates must have at least one year of skilled work experience in Canada within the past three years. The work experience must be in a National Occupational Classification (NOC) skill level 0, A, or B occupation.
– Language Proficiency: Candidates must demonstrate proficiency in English or French by taking a designated language test (such as IELTS or CELPIP) and achieving the minimum required scores.
– Education: While there is no specific education requirement for the CEC, having a Canadian educational credential can contribute to additional points in the CRS.
– Admissibility: Candidates must meet the admissibility requirements, including health and security checks.
iii. Application Process:
The application process for the CEC involves the following steps:
– Create an Express Entry Profile: Candidates create an Express Entry profile and indicate their interest in the CEC. The profile includes information about their work experience, language proficiency, education, and other relevant details.
– Comprehensive Ranking System (CRS) Score: Candidates are assigned a CRS score based on their profile information. The CRS score determines their ranking in the Express Entry pool.
– Invitation to Apply (ITA): Candidates with high CRS scores are invited to apply for permanent residency through regular draws conducted by the Canadian government.
– Submitting the Application: Candidates who receive an ITA have 60 days to submit a complete application for permanent residency, including supporting documents and fees.
iv. Selection Factors:
The CEC uses a points-based system to assess candidates based on various selection factors, including:
– Canadian Work Experience: More years of Canadian work experience result in more points.
– Language Proficiency: Higher language test scores contribute to additional points.
– Education: Having a Canadian educational credential can contribute to additional points.
– Age: Younger candidates receive more points.
– Adaptability: Factors such as previous study or work experience in Canada, a job offer, or family connections in Canada can contribute to additional points.
5:Provincial Nominee Programs (PNPs): A Pathway to Canadian Permanent Residency

Provincial Nominee Programs (PNPs) play a crucial role in Canadian immigration, offering individuals an alternative pathway to obtain permanent residency. This article provides an overview of PNPs, including their purpose, eligibility criteria, application process, and benefits.
i. Purpose and Benefits:
PNPs allow provinces and territories in Canada to address their specific economic and demographic needs by nominating skilled workers for immigration. The key benefits of PNPs include:
– Tailored Immigration Pathways: Each province and territory has its own PNP, allowing them to design immigration pathways based on their unique economic and demographic requirements.
– Provincial Nomination: Candidates nominated by a province or territory through a PNP receive additional Comprehensive Ranking System (CRS) points, significantly increasing their chances of receiving an Invitation to Apply (ITA) for permanent residency.
– Regional Opportunities: PNPs provide opportunities for individuals to settle and contribute to the development of specific regions within Canada.
ii. Eligibility Criteria:
Eligibility criteria for PNPs vary depending on the province or territory. However, common requirements include:
– Work Experience: Candidates must have relevant work experience in an occupation that meets the specific needs of the province or territory.
– Education: Candidates must meet the educational requirements set by the province or territory, which may include a minimum level of education or specific credentials.
– Language Proficiency: Proficiency in English or French is typically required, and candidates may need to provide language test results.
– Connection to the Province: Some PNPs require candidates to have a genuine intention to live and work in the nominating province or territory, which can be demonstrated through previous work or study experience, family connections, or a job offer.
iii. Application Process:
The application process for PNPs generally involves the following steps:
– Expression of Interest: Candidates express their interest in a specific PNP by submitting an Expression of Interest (EOI) or an online application.
– Provincial Nomination: If selected, candidates receive a provincial nomination, which provides them with additional CRS points in the Express Entry system.
– Application for Permanent Residency: Candidates with a provincial nomination can then apply for permanent residency to the federal government, providing the necessary documents and paying the required fees.
iv. Selection Factors:
Selection factors for PNPs vary among provinces and territories. Common factors include:
– Work Experience: Relevant work experience in an occupation in demand in the province or territory.
– Language Proficiency: Proficiency in English or French, usually demonstrated through language test results.
– Education: Meeting the educational requirements set by the province or territory.
– Adaptability: Factors such as previous work or study experience in the province or territory, family connections, or a job offer may contribute to additional points.
– Eligibility: PNPs have different eligibility criteria, including work experience, education, language proficiency, and connections to the province. Candidates can apply directly to a PNP or through the Express Entry system.
6:Eligibility for Canada Immigration: Requirements and Pathways
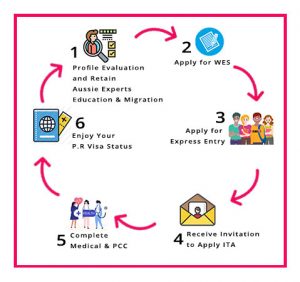
Canada offers various immigration pathways for individuals seeking to make Canada their new home. This article provides an overview of the general eligibility requirements for immigration to Canada, including key factors such as language proficiency, education, work experience, and financial stability.
i. Language Proficiency:
Proficiency in English or French is a crucial requirement for most Canadian immigration programs. Applicants are typically required to take language tests, such as the International English Language Testing System (IELTS) or the Canadian English Language Proficiency Index Program (CELPIP), to demonstrate their language skills.
ii. Education:
Education plays a significant role in the Canadian immigration process. Most programs require applicants to have completed a minimum level of education, such as a high school diploma or a post-secondary degree. Educational credentials obtained outside of Canada may need to be assessed by a designated organization to determine their Canadian equivalency.
iii. Work Experience:
Having relevant work experience is often a requirement for Canadian immigration programs. Applicants are typically required to demonstrate a certain number of years of full-time or equivalent part-time work experience in a skilled occupation. The work experience must be within a specific timeframe, usually the past 10 years, and should be classified under the National Occupational Classification (NOC) system.
iv. Financial Stability:
Applicants are required to demonstrate that they have sufficient funds to support themselves and their family members upon arrival in Canada. The specific amount varies depending on the number of family members and the chosen immigration program. Proof of financial stability can be in the form of bank statements, employment letters, or other supporting documents.
v. Immigration Pathways:
Canada offers several immigration pathways, including the Express Entry system, Provincial Nominee Programs (PNPs), and Family Sponsorship programs. Each pathway has its own specific eligibility criteria and requirements. It is important for applicants to research and determine which pathway aligns with their qualifications and goals.
7:Language Proficiency Requirements for Canadian Immigration
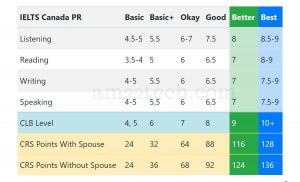
Language proficiency is a crucial factor in Canadian immigration, as it plays a significant role in successful integration into Canadian society. This article provides an overview of the language proficiency requirements for Canadian immigration, including the accepted language tests, minimum score requirements, and the importance of language skills in the immigration process.
i. Accepted Language Tests:
The two accepted language tests for Canadian immigration are the International English Language Testing System (IELTS) and the Canadian English Language Proficiency Index Program (CELPIP) for English proficiency, and the Test d’évaluation de français (TEF) for French proficiency. These tests assess the candidate’s language skills in reading, writing, listening, and speaking.
ii. Minimum Score Requirements:
Different immigration programs and categories have specific minimum score requirements for language proficiency. For example, the Federal Skilled Worker Program (FSWP) requires a minimum Canadian Language Benchmark (CLB) level 7 in all language abilities for English or French. The Canadian Experience Class (CEC) and Provincial Nominee Programs (PNPs) may have different language requirements, so it is important to check the specific program requirements.
iii. Importance of Language Skills:
Language skills are essential for successful integration into Canadian society. Proficiency in English or French enables immigrants to communicate effectively, find employment opportunities, access education and healthcare services, and participate fully in their communities. Language skills also contribute to higher chances of securing employment and career advancement in Canada.
iv. Language Proficiency Points in Express Entry:
In the Express Entry system, language proficiency is a crucial factor in the Comprehensive Ranking System (CRS) score calculation. Higher language test scores result in more CRS points, which can significantly increase an applicant’s chances of receiving an Invitation to Apply (ITA) for permanent residency. Therefore, investing time and effort in improving language skills can have a positive impact on the overall immigration process.
v. Language Training and Support:
Canada offers various language training programs and resources to help immigrants improve their language skills. These include language classes, settlement services, and community programs. Taking advantage of these resources can enhance language proficiency and facilitate successful integration into Canadian society.
4. Educational Credential Assessment (ECA):
To ensure the recognition of foreign educational credentials, candidates must obtain an Educational Credential Assessment (ECA) from designated organizations. This assessment verifies the equivalency of foreign degrees, diplomas, or certificates to Canadian standards.
8:Educational Credential Assessment (ECA) for Canadian Immigration: Understanding its Importance

The Educational Credential Assessment (ECA) is a crucial step in the Canadian immigration process, particularly for individuals with foreign educational credentials. This article provides an overview of the Educational Credential Assessment, its significance in Canadian immigration, the organizations responsible for conducting ECAs, and the process involved.
i. What is an Educational Credential Assessment (ECA)?
An Educational Credential Assessment is an evaluation of foreign educational credentials to determine their Canadian equivalency. It helps Canadian immigration authorities understand the educational qualifications of applicants and ensures that their credentials meet the standards set by Canadian educational institutions and employers.
ii. Importance of ECA in Canadian Immigration:
The ECA is essential for several immigration programs, including the Federal Skilled Worker Program (FSWP), the Canadian Experience Class (CEC), and some Provincial Nominee Programs (PNPs). It provides a standardized assessment of an applicant’s educational qualifications, allowing immigration authorities to accurately evaluate their eligibility for immigration and assign appropriate points in the selection process.
iii. Organizations Responsible for ECA:
There are designated organizations authorized by Immigration, Refugees and Citizenship Canada (IRCC) to conduct ECAs. These organizations include:
– Comparative Education Service (CES) – University of Toronto School of Continuing Studies
– International Credential Assessment Service of Canada (ICAS)
– World Education Services (WES)
– International Qualifications Assessment Service (IQAS)
– Medical Council of Canada (for medical professionals)
iv. ECA Process:
The ECA process typically involves the following steps:
– Submission of Documents: Applicants need to submit their educational documents, such as transcripts, diplomas, and degrees, to the designated ECA organization.
– Evaluation: The organization assesses the documents and compares them to Canadian educational standards to determine their equivalency.
– ECA Report: Once the evaluation is complete, the organization issues an ECA report, which outlines the Canadian equivalency of the applicant’s educational credentials.
v. Using the ECA Report:
The ECA report is a crucial document that applicants can use to support their immigration application. It provides evidence of their educational qualifications and helps immigration authorities understand the level of education attained. The ECA report is typically valid for a specific period, so applicants should ensure its validity during the application process.
5. Comprehensive Ranking System (CRS) Score:
The CRS score is a crucial factor in Express Entry. It evaluates candidates based on factors such as age, education, work experience, language proficiency, and adaptability. Maximizing CRS points through various strategies, such as improving language skills or obtaining a job offer, can significantly enhance the chances of receiving an ITA.
9:Comprehensive Ranking System (CRS) Score: Understanding its Significance in Canadian Immigration
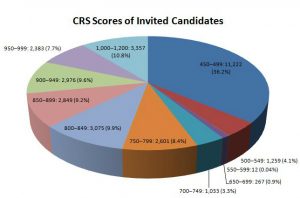
The Comprehensive Ranking System (CRS) score is a crucial component of the Canadian immigration system, specifically the Express Entry program. This article provides an in-depth understanding of the CRS score, its significance in the immigration process, and strategies to improve one’s CRS score.
i. What is the Comprehensive Ranking System (CRS) Score?
The CRS score is a points-based system used by Immigration, Refugees and Citizenship Canada (IRCC) to rank candidates in the Express Entry pool. It evaluates various factors, including age, education, work experience, language proficiency, and adaptability, to determine an applicant’s eligibility for permanent residency.
ii. Factors Considered in CRS Score Calculation:
The CRS score is calculated based on the following factors:
– Core Human Capital Factors: These include age, level of education, official language proficiency (English or French), and Canadian work experience.
– Spouse or Common-Law Partner Factors: If applicable, the spouse’s or common-law partner’s education, language proficiency, and Canadian work experience are also considered.
– Skill Transferability Factors: These factors assess the combination of an applicant’s education, language proficiency, and work experience to determine their potential for success in the Canadian labor market.
– Additional Factors: Additional points can be earned through factors such as a provincial nomination, a valid job offer, or Canadian education.
iii. Significance of CRS Score:
The CRS score plays a vital role in the Express Entry system. It determines a candidate’s ranking in the pool and their chances of receiving an Invitation to Apply (ITA) for permanent residency. Higher CRS scores increase the likelihood of receiving an ITA, as candidates with the highest scores are typically invited to apply during regular draws conducted by the Canadian government.
iv. Strategies to Improve CRS Score:
Candidates can employ several strategies to enhance their CRS score:
– Improving Language Proficiency: Investing time and effort in language training and achieving higher language test scores can significantly boost CRS points.
– Enhancing Education: Pursuing further education or obtaining Canadian educational credentials can contribute to additional CRS points.
– Gaining Canadian Work Experience: Acquiring work experience in Canada, especially in skilled occupations, can increase CRS points.
– Obtaining a Provincial Nomination: A nomination from a province or territory through a Provincial Nominee Program (PNP) can provide a substantial CRS score boost.
– Securing a Valid Job Offer: A valid job offer from a Canadian employer can result in additional CRS points.
v. Settlement and Integration:
Preparing for settlement and integration in Canada is essential for a smooth transition. Consider the following:
10:Settlement and Integration in Canada: A Guide for Newcomers

Settlement and integration are crucial aspects of the immigration journey to Canada. This article serves as a comprehensive guide for newcomers, providing valuable information and resources to facilitate a smooth transition and successful integration into Canadian society. From pre-arrival preparations to finding housing, accessing healthcare, and building a support network, this article covers essential aspects of settlement and integration in Canada.
i. Preparing for Arrival:
Before arriving in Canada, it is important to make necessary preparations to ensure a smooth transition. This section covers key aspects such as:
– Researching Canadian Culture and Society: Familiarize yourself with Canadian customs, values, and social norms to better understand and adapt to the Canadian way of life.
– Gathering Important Documents: Ensure you have all the necessary documents, such as passports, visas, and immigration papers, readily available for a hassle-free entry into Canada.
– Financial Planning: Develop a budget, understand the cost of living in Canada, and make arrangements for accessing funds during the initial settlement period.
ii. Finding Housing:
Securing suitable housing is a top priority for newcomers. This section provides guidance on:
– Rental Market Overview: Understand the rental market in Canada, including different types of housing, rental agreements, and tenant rights.
– Searching for Accommodation: Explore various resources and platforms to find suitable housing options, such as rental websites, real estate agents, and community networks.
– Settling In: Learn about essential tasks upon moving into a new home, including setting up utilities, registering for services, and familiarizing yourself with the neighborhood.
iii. Accessing Healthcare:
Understanding Canada’s healthcare system and accessing medical services is crucial for newcomers. This section covers:
– Overview of the Healthcare System: Learn about Canada’s publicly funded healthcare system, including coverage, primary care providers, and emergency services.
– Registering for Health Insurance: Understand the process of obtaining health insurance coverage, such as the provincial health card, and the importance of timely registration.
– Finding Healthcare Providers: Explore resources to find doctors, dentists, and other healthcare professionals in your area, and understand how to make appointments and access healthcare services.
iv. Building a Support Network:
Creating a support network is essential for a successful integration into Canadian society. This section highlights:
– Community Resources: Discover local community organizations, immigrant services, and cultural associations that provide support, information, and resources for newcomers.
– Language and Cultural Programs: Take advantage of language classes, cultural programs, and workshops to improve language skills, learn about Canadian culture, and connect with other newcomers.
– Networking Opportunities: Engage in networking events, professional associations, and online platforms to expand your professional network and explore job opportunities.
11:Research and Planning: Essential Steps for a Successful Move to Canada

Planning a move to Canada requires careful research and preparation to ensure a smooth transition and successful settlement. This article provides a comprehensive guide on the importance of research and planning, offering valuable insights and resources to help individuals navigate the process effectively.
i. Understanding Canadian Culture and Society:
Before moving to Canada, it is crucial to familiarize yourself with Canadian customs, values, and social norms. This section covers:
– Cultural Awareness: Learn about Canadian traditions, etiquette, and social norms to better understand and adapt to the Canadian way of life.
– Diversity and Inclusion: Explore Canada’s multicultural society and embrace the diversity of its people, languages, and traditions.
– Canadian Laws and Regulations: Familiarize yourself with Canadian laws, rights, and responsibilities to ensure compliance and a smooth integration into the legal system.
ii. Researching Provinces and Territories:
Canada is a vast country with diverse regions, each offering unique opportunities and characteristics. This section highlights:
– Provincial/Territorial Profiles: Explore the different provinces and territories, their economies, climates, job markets, and quality of life to determine the best fit for your needs and aspirations.
– Cost of Living: Research the cost of living in different regions, including housing, transportation, healthcare, and education, to plan your budget effectively.
– Provincial Nominee Programs (PNPs): Understand the PNPs offered by each province or territory, as they may have specific immigration pathways and criteria tailored to their economic needs.
iii. Financial Planning:
Financial planning is crucial to ensure a smooth transition and a stable start in Canada. This section covers:
– Budgeting: Develop a comprehensive budget that takes into account your anticipated expenses, including accommodation, transportation, groceries, utilities, and healthcare.
– Currency Exchange: Understand the process of exchanging currency and explore options for transferring funds to Canada.
– Banking and Taxation: Research Canadian banking options, open a bank account, and familiarize yourself with the Canadian tax system to ensure compliance.
iv. Healthcare and Insurance:
Accessing healthcare services and obtaining appropriate insurance coverage is essential for your well-being in Canada. This section provides guidance on:
– Canadian Healthcare System: Understand the publicly funded healthcare system in Canada, including coverage, primary care providers, and emergency services.
– Health Insurance: Explore options for obtaining health insurance coverage, such as provincial health plans, private insurance, or employer-sponsored plans, depending on your eligibility and needs.
12:Networking and Support: Building Connections for a Successful Transition to Canada

Networking and support play a crucial role in facilitating a smooth transition and successful integration into Canadian society. This article provides valuable insights and strategies for newcomers to Canada on how to build a professional network, access support services, and leverage community resources to enhance their settlement experience.
i. Importance of Networking:
Networking is a powerful tool for career advancement, accessing job opportunities, and gaining valuable insights into the Canadian job market. This section highlights:
– Professional Associations: Join industry-specific professional associations and attend networking events to connect with professionals in your field and expand your professional network.
– Online Networking: Utilize professional networking platforms such as LinkedIn to connect with professionals, join relevant groups, and showcase your skills and experience.
– Informational Interviews: Conduct informational interviews with professionals in your desired field to gain insights into the Canadian job market, industry trends, and potential job opportunities.
ii. Community Support Services:
Canada offers a wide range of support services and resources to assist newcomers in their settlement journey. This section covers:
– Immigrant Settlement Agencies: Connect with local immigrant settlement agencies that provide a range of services, including language training, employment support, and assistance with housing and healthcare.
– Cultural Associations: Engage with cultural associations and community organizations that represent your cultural background to connect with individuals who share similar experiences and provide a sense of belonging.
– Mentorship Programs: Seek out mentorship programs that pair newcomers with established professionals in their field, providing guidance, advice, and support in navigating the Canadian job market.
iii. Volunteering and Community Engagement:
Getting involved in volunteering and community engagement activities not only helps newcomers contribute to their communities but also provides opportunities to expand their network and gain Canadian work experience. This section explores:
– Volunteering Opportunities: Research local volunteer organizations and initiatives that align with your interests and skills, allowing you to make a positive impact while building connections.
– Community Events and Workshops: Attend community events, workshops, and seminars to meet like-minded individuals, learn about Canadian culture, and expand your knowledge and skills.
13:Navigating the Job Search Process in Canada: Strategies for Success

Finding employment in Canada is a crucial step towards a successful settlement and integration into Canadian society. This article provides valuable guidance and strategies for newcomers on how to navigate the job search process effectively and increase their chances of securing employment in Canada.
i. Understanding the Canadian Job Market:
Before embarking on your job search, it is essential to familiarize yourself with the Canadian job market. This section covers:
– Labor Market Information: Research current labor market trends, job demand, and growth sectors in the region where you plan to settle. Websites such as Job Bank and provincial job boards provide valuable information on job opportunities and labor market conditions.
– Occupational Licensing and Certification: Determine if your profession or trade requires specific licensing or certification in Canada. Research the regulatory bodies and requirements for obtaining the necessary credentials.
– Canadian Resume and Cover Letter: Adapt your resume and cover letter to meet Canadian standards. Highlight your relevant skills, qualifications, and work experience in a clear and concise manner.
ii. Online Job Search Strategies:
Online job search platforms are a valuable resource for finding job opportunities in Canada. This section explores:
– Job Search Websites: Utilize popular job search websites such as Indeed, LinkedIn, and Workopolis to search for job postings in your field. Create a professional profile on LinkedIn to showcase your skills and connect with potential employers.
– Company Websites: Visit the websites of companies you are interested in working for. Many organizations post job openings directly on their websites.
– Job Alerts and Notifications: Set up job alerts on job search websites to receive notifications about new job postings that match your criteria.
iii. Networking and Professional Connections:
Networking is a powerful tool for accessing the hidden job market and gaining insider information about job opportunities. This section covers:
– Professional Associations and Events: Join industry-specific professional associations and attend networking events to connect with professionals in your field. Networking events, career fairs, and industry conferences provide opportunities to meet potential employers and expand your professional network.
– Informational Interviews: Conduct informational interviews with professionals in your desired field to gain insights into the Canadian job market, industry trends, and potential job opportunities. These interviews can also help you build valuable connections and referrals.
iv. Tailoring Your Job Search:
Customizing your job search approach can significantly increase your chances of success. This section explores:
– Targeted Applications: Tailor your resume and cover letter to match the specific requirements of each job application. Highlight relevant skills, experiences, and achievements that align with the job description.
– Transferable Skills: Emphasize transferable skills that are applicable to the Canadian job market. Highlight your adaptability, teamwork, communication, and problem-solving skills.
– Volunteer Work and Internships: Consider volunteering or participating in internships to gain Canadian work experience, expand your network, and enhance your resume.
